Eating Disorders: Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa & Binge Eating
“Finding freedom in food.
Breaking barriers with every bite.
& Let’s challenge stigma and promote understanding.
around nutrition and eating disorders”.
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions characterized by disturbances in eating behaviors, body image, and emotions. These disorders can have serious physical and psychological consequences and require professional intervention and support for healing and recovery.
Types of Eating Disorders:
1. Anorexia Nervosa: Severely limiting food, fearing weight gain, and having a wrong view of your body, along with extreme exercise and obsession with food and weight control.
2. Bulimia Nervosa: Recurrent episodes of binge eating, followed by compensatory behaviors like self-induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives or diuretics, fasting, or excessive exercise.
3. Binge Eating Disorder (BED): Recurrent consumption of large quantities of food in a short period, accompanied by a sense of loss of control.
Genetic Predisposition: Having a family history of diabetes increases the likelihood of developing the disease and poor lifestyle certainly worsens the prognosis.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Excess body weight, particularly fat on the abdomen and physical inactivity are major contributors to type 2 diabetes. Adipose tissue ie visceral fat increases inflammation impairing insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. This resistance forces the pancreas to produce more insulin to compensate, leading to elevated blood sugar levels over time. This reaction often leads to dark skin pigmentation seen on neck-underarms -acanthosis nigricans.
Poor Diet: A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can contribute to insulin resistance and weight gain, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Factors: Gestational diabetes can develop during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that affect insulin sensitivity. Women who develop gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, as do their children.
Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to obesity, insulin resistance, and poor blood sugar control. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss or maintenance, and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Stress: Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, leading to increased blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises can help mitigate the impact of stress on diabetes risk.
Sleep Disorders: Poor sleep quality, sleep deprivation, and untreated sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea can disrupt hormonal balance, increase insulin resistance, and raise the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What causes Anorexia Nervosa:
1. Genetics
2. Psychological Factors: anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, perfectionism, body dissatisfaction, trauma, or difficulty coping with emotions.
3. Sociocultural Influences: Societal pressures to attain a thin body ideal, media portrayal of thinness, and cultural attitudes toward food, weight, and beauty can contribute to the development of anorexia nervosa.
4. Personality Traits: Obsessiveness, rigidity, or a desire for control.
5. Life Transitions or Stressful Events like puberty, starting college, changes in relationships, trauma, abuse, or loss.
Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa:

Acne
Brittle hair & nails

Denial of eating disorder

Distorted Body Image

Excessive Exercise

Fear of weight gain

Food Obsessions
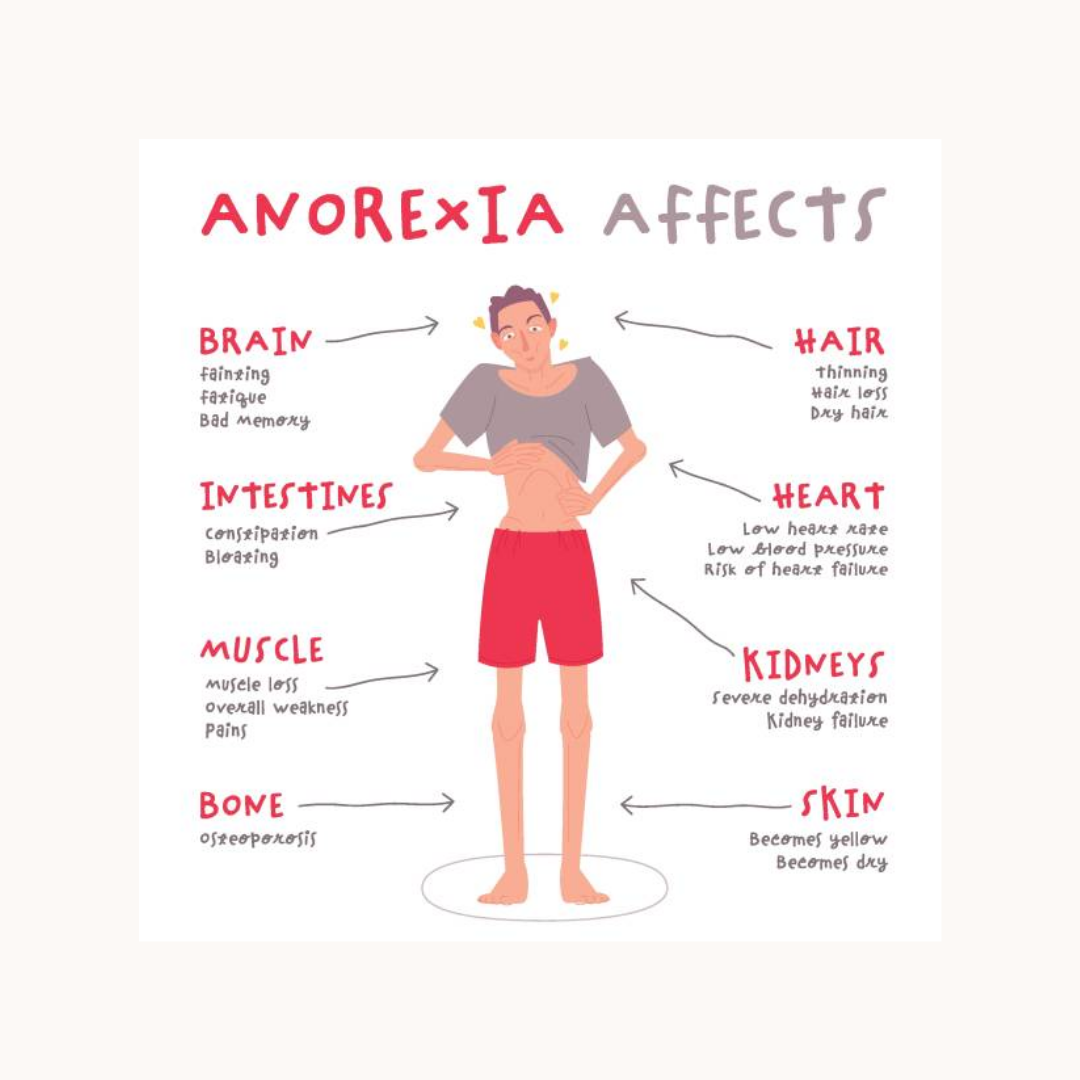
Physical Symptoms

Restrictive eating patterns

Sensitivity to cold

Social Withdrawal
What causes Bulimia Nervosa:
1. Genetics
2. Psychological Factors -low self-esteem, body dissatisfaction, perfectionism, impulsivity, anxiety, depression, or difficulty coping with emotions; trauma, abuse, or stressful life events.
3. Dieting and Weight Concerns -Restrictive dieting or attempts to lose weight may trigger episodes of binge eating.
4. Negative Body Image
Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa::

Anxiety

Binge eating

Dental problems

Depression

Fear of weight gain

Guilt
Gut issues

Irregular menstrual cycle

Mood swings

Secretive Behavior
Self induced vomiting

Social withdrawl
Our Program Features:
- Diet therapy to manage eating disorders with correction of nutritional status.
- Video / In-Clinic consultation with Dr. Zubeda Tumbi.
- Follow-up Consultation with Dr. Tumbi Every 10th – 12th day.
- We have personalized, customized diet & lifestyle plans.
- Team Support: Monday to Saturday; 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM on WhatsApp, Phone & Email.
- Our supportive community outreach programs: a unique feature begun by Dr. Tumbi will help you to connect, share experiences with likeminded people in a group therapy.
- Tips on stress management techniques, reducing screen time and improving sleep hygiene are important tools in this health journey.
At Health Watch Nutrition Clinic: Our Eating Disorder Management Program is designed to provide nutritional counseling, balanced diets and compassionate evidence-based care because we understand that each patient’s journey with eating disorder is unique. We encourage patients to challenge food-related fears, normalize eating behaviors, and restore physical health with personalized nutrition guidance. The personalized approach by Dr. Zubeda Tumbi and her team helps you reach your health goals that impacts your health holistically.

